
This is why you start assessing your patient with an airway, breathing, circulation approach, because that's the most life-threatening order in which problems present. To survive, we need to get oxygen from the air into our blood, in order to supply the tissues. Dead space is important to think about, especially in paediatrics.Ventilation/Perfusion matching is everything (sort of).It should therefore not be forgotten in the intensive care setting. A correct measurement and calculation of the dead space will give valuable information on the ventilatory support of the critically ill patient and can also be a valuable diagnostic tool. However, both are subjected to potential errors that have to be considered to make a dead space recording meaningful. The recording of dead spaces can be done according to the Riley three-compartment model or by analysis of the expired CO2 curve. The dead spaces 2-5 are called physiological dead space. pulmonary embolus (alveolar dead space), 4/ Excessive ventilation of alveoli in relation to their perfusion that can be seen in chronic obstructive lung disease (another form of alveolar dead space), and 5/ So called "shunt dead space" that is an erroneous description of right to left lung shunt that brings the higher CO2 concentration in venous blood to the arterial side thereby producing an arterial-to-end-tidal CO2 difference. This is because dead space is affected by a number of factors: 1) tubings and valves that the subject has to rebreath through (apparatus dead space), 2/ Airways (anatomical dead space), 3/ Non-perfused but ventilated alveoli, e.g.
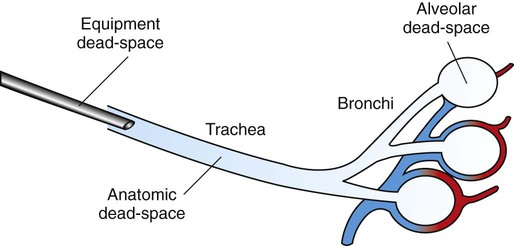
Moreover, dead space will give insight into the matching of ventilation and perfusion. Realising that CO2 retention can be an effect not only of low total ventilation but also of increased dead space is one important information. The recording of dead space will give information on how much of total ventilation that reaches both ventilated and perfused alveoli and thus allows gas exchange between alveoli and pulmonary blood.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
